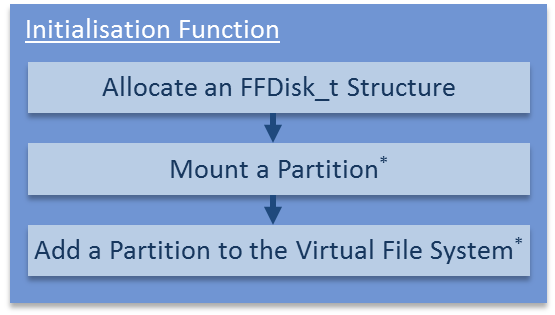
在媒体驱动器初始化函数中执行的操作
(*可选步骤)
媒体驱动程序初始化函数必须分配
FF_Disk_t
结构体,以供媒体使用。
FF_Disk_t 结构体包含指向 FF_IOManager_t 结构体的指针。
FF_IOManager_t 结构体的创建需调用
FF_CreateIOManager()。
为方便起见,媒体驱动程序还可以
选择性在媒体上挂载分区,
并添加挂载
分区到 FreeRTOS-Plus-FAT 的虚拟文件系统。 在初始化函数中执行
这两个可选步骤之后,
应用程序编写者便无需显式执行这些步骤。 右图
显示了执行这些可选步骤的媒体驱动程序的
初始化函数。
工作示例
以下示例大致描述了
FreeRTOS-Plus-FAT RAM 磁盘驱动程序使用的媒体驱动程序初始化函数。 如需包含更多错误检查的
完整版本,请参阅
/FreeRTOS-Plus/Source/FreeRTOS-Plus-FAT/portable/common/ff_ramdisk.c。
#define ramSECTOR_SIZE 512UL
#define ramPARTITION_NUMBER 0
FF_Disk_t *FF_RAMDiskInit( char *pcName,
uint8_t *pucDataBuffer,
uint32_t ulSectorCount,
size_t xIOManagerCacheSize )
{
FF_Error_t xError;
FF_Disk_t *pxDisk = NULL;
FF_CreationParameters_t xParameters;
configASSERT( ( xIOManagerCacheSize % ramSECTOR_SIZE ) == 0 );
configASSERT( ( xIOManagerCacheSize >= ( 2 * ramSECTOR_SIZE ) ) );
pxDisk = ( FF_Disk_t * ) pvPortMalloc( sizeof( FF_Disk_t ) );
if( pxDisk != NULL )
{
memset( pxDisk, '�', sizeof( FF_Disk_t ) );
pxDisk->pvTag = ( void * ) pucDataBuffer;
pxDisk->ulSignature = ramSIGNATURE;
pxDisk->ulNumberOfSectors = ulSectorCount;
memset (&xParameters, '�', sizeof xParameters);
xParameters.pucCacheMemory = NULL;
xParameters.ulMemorySize = xIOManagerCacheSize;
xParameters.ulSectorSize = ramSECTOR_SIZE;
xParameters.fnWriteBlocks = prvWriteRAM;
xParameters.fnReadBlocks = prvReadRAM;
xParameters.pxDisk = pxDisk;
xParameters.pvSemaphore = ( void * ) xSemaphoreCreateRecursiveMutex();
xParameters.xBlockDeviceIsReentrant = pdTRUE;
pxDisk->pxIOManager = FF_CreateIOManger( &xParameters, &xError );
if( ( pxDisk->pxIOManager != NULL ) && ( FF_isERR( xError ) == pdFALSE ) )
{
pxDisk->xStatus.bIsInitialised = pdTRUE;
xError = prvPartitionAndFormatDisk( pxDisk );
if( FF_isERR( xError ) == pdFALSE )
{
pxDisk->xStatus.bPartitionNumber = ramPARTITION_NUMBER;
xError = FF_Mount( pxDisk, ramPARTITION_NUMBER );
}
if( FF_isERR( xError ) == pdFALSE )
{
FF_FS_Add( pcName, pxDisk->pxIOManager );
}
}
else
{
FF_RAMDiskDelete( pxDisk );
pxDisk = NULL;
}
}
return pxDisk;
}
The outline of a media driver's initialisation function
Copyright (C) Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.